
Positive radial velocity means the star is receding from the Sun, negative that it is approaching. To observe such a change in color, the object would have to be traveling at approximately 5200 km/s, or about 75 times faster than the speed record for the fastest manmade space probe.Īmong the nearby stars, the largest radial velocities with respect to the Sun are +308 km/s (BD-15☄041, also known as LHS 52, 81.7 light-years away) and -260 km/s (Woolley 9722, also known as Wolf 1106 and LHS 64, 78.2 light-years away). The Doppler effect causes a train whistle, car, or airplane to sound higher when it is moving towards you, and lower when it is moving away from you. Light emitted from a source moving toward us experiences a blueshift. Since light is also a wave, a moving light source will experience the Doppler effect. The waves can be ripples on the surface of a pond or sound waves traveling through the air.
The pulsar PSR1913+16 is a neutron star which rotates around itself 17 times per second. The Doppler effect applies to any source of waves. Doppler observed that as a train is approaching us and we are stationary, the sound of the train gets louder as the frequency of the waves increases. Since blue light has a higher frequency than red light, the spectral lines of an approaching astronomical light source exhibit a blueshift and those of a receding astronomical light source exhibit a redshift.ĭoppler effect, yellow (~575 nm wavelength) ball appears greenish (blueshift to ~565 nm wavelength) approaching observer, turns orange (redshift to ~585 nm wavelength) as it passes, and returns to yellow when motion stops. A more recent example can be found in contemporary astronomy. The Doppler effect is of intense interest to astronomers who use the information about the shift in frequency of electromagnetic waves produced by moving. The Doppler effect is recognizable in the fact that the absorption lines are not always at the frequencies that are obtained from the spectrum of a stationary light source. They exhibit absorption lines at well defined frequencies that are correlated with the energies required to excite electrons in various elements from one level to another. The use of the Doppler effect for light in astronomy depends on our knowledge that the spectra of stars are not homogeneous.
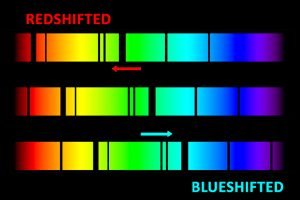
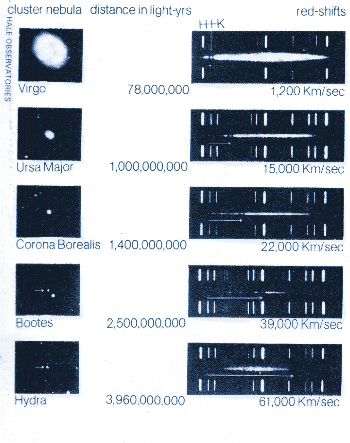
Redshift of spectral lines in the optical spectrum of a supercluster of distant galaxies (right), as compared to that of the Sun (left) This is used to detect if an apparently single star is, in reality, a close binary and even to measure the rotational speed of stars and galaxies. Definition: Doppler Effect refers to the change in wave frequency during the relative motion between a wave source and its observer. It has been used to measure the speed at which stars and galaxies are approaching or receding from us, that is, the radial velocity. \)Īstronomy The Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves such as light is of great use in astronomy and results in either a so-called redshift or blueshift.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
